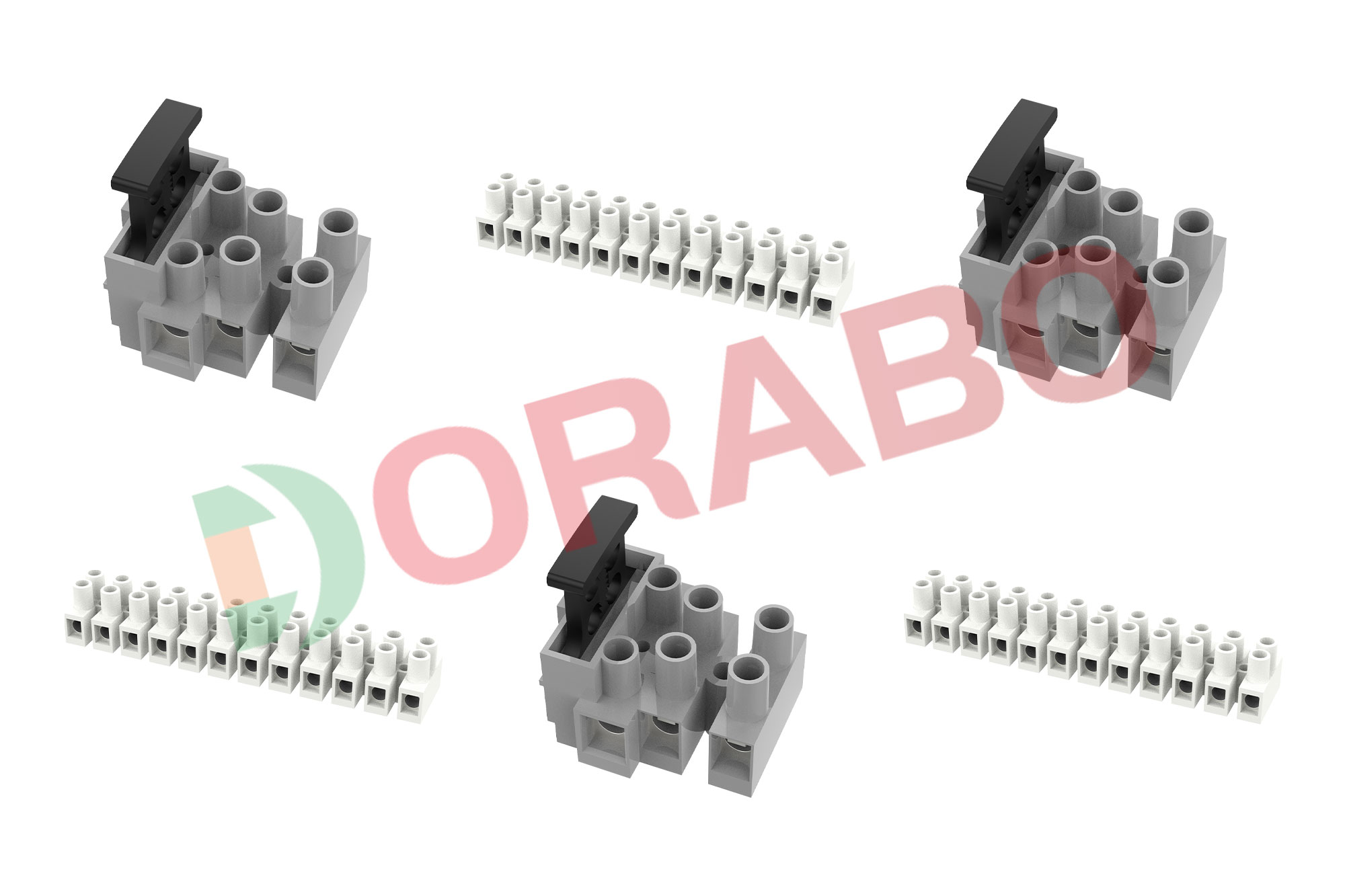
Terminal blocks consist of modular housings and insulators used to hold two or more wires together in electrical systems that require secure connections. Terminal blocks, also known as screw terminals, terminal connectors, or connecting terminals, provide engineers with semi-permanent wire connections that provide organized and simplified inspection or repair capabilities in the field.
Although components are widely used in numerous applications, it is still important to have a basic understanding of common terminal block types and sizes before making a final selection. While engineers may know their overall system voltage and current requirements when implementing terminal blocks, there are other important factors to be aware of during the design phase:
1. Rated current. Often the most critical specification to consider in the terminal design, the current rating is based on three aspects: the electrical conductivity of the terminal, the cross-sectional area, and the corresponding temperature rise. When operating at excessively high currents, overheating and damage to the junction box can occur, which can pose serious safety concerns. It is recommended to select terminals with a current rating of at least 150% of the maximum current expected in the system.
2. Rated voltage. Like the current rating, the voltage rating of the junction box must be greater than the maximum system voltage and should also take into account any voltage surges that may be present in the end system. The voltage rating depends in part on the dielectric strength and spacing of the junction box enclosure.
3. Number of poles. Used to specify the number of individual circuits that the terminal block will hold based on the application needs. Terminal blocks are typically available in pole counts from single pole up to 24 poles.
4. Pitch. It is defined as the distance from the center of the magnetic pole to the magnetic pole, expressed as 2.54mm, 3.81mm, 5.0mm, etc. Spacing is determined by the overall rating of the terminal block, which involves factors such as creepage distance, voltage/current, and clearance.
5. Wire size/type. To ensure that the wires physically fit into the junction box enclosure, the junction box lists the wire sizes or gauges that the module can accept, specified in North America in American Wire Gauge units. Each terminal block is generally able to accept a flexible range of wire sizes.
Also, the type of wire used should be considered based on the type of module. Solid wire is usually paired with push-fit terminals, while stranded or multi-wire is ideal for screw terminals.















 Contact us
Contact us Language
Language


